CV measurements are most often used to assess the near-equilibrium properties of an electrode including:
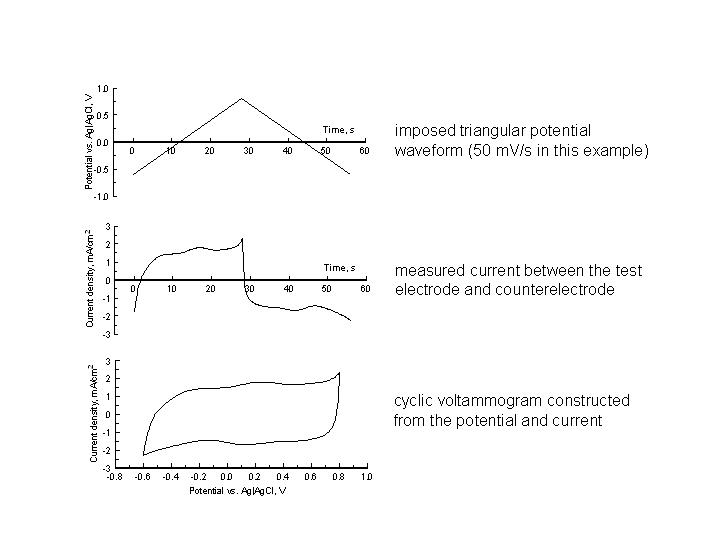
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) is a 3-electrode measurement in which the potential of the test electrode is driven
at a constant sweep rate with respect to a non-current carrying reference electrode. The current required to
change the test electrode potential is provided by a counterelectrode and the CV is constructed from the
test electrode potential and current. It is important to appreciate that the CV response, for any electrode,
can appear very different depending on the sweep rate, the geometric area of the electrode, and the
roughness of the electrode, even though the electrochemical reactions are unchanged.
Making A CV Measurement
